Antibiotic Susceptibility of Salmonella Species Isolated from Stool Samples of Patients Attending Ahmadu Bello University, Medical Centre, Zaria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70882/josrar.2025.v2i4.93Keywords:
Salmonella, Antibiotics resistance, ABUMC, ZariaAbstract
Salmonella infection remains a major global public health concern. The effective treatment of salmonellosis and other enteric infections has been severely compromised by the emergence of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella strains, largely due to decades of indiscriminate and inappropriate antibiotic use. This study was designed to isolate Salmonella species from stool samples of patients attending the Ahmadu Bello University Medical Centre, Zaria, and to evaluate their antibiotic susceptibility patterns. A total of 100 stool samples were collected and screened for Salmonella. Initial enrichment was carried out using Selenite F broth, followed by inoculation onto Salmonella-Shigella agar, and subsequent subculture onto nutrient agar slants for storage and pure culture preparation. The isolates were subjected to a series of biochemical tests, including motility, catalase, citrate utilization, sugar fermentation, and methyl red–Voges-Proskauer (MR-VP) tests. Out of the 100 samples analyzed, 17 (17.0%) tested positive for Salmonella. Antibiotic susceptibility testing revealed the highest sensitivity to ceftazidime (64.7%) and ceftriaxone (47.1%), while resistance was most pronounced against ciprofloxacin (76.5%), amoxicillin (70.6%), chloramphenicol (52.9%), and gentamicin (47.1%). Although no statistically significant associations were observed between infection rate and socio-demographic or risk factors, a higher prevalence was noted among male patients, children aged 4–12 years, individuals consuming unwashed raw vegetables, households with pets, persons exposed to livestock and their waste, those who washed hands infrequently, individuals not using hand sanitizers, and those relying on well water as their primary drinking source. Strengthening public awareness on safe food handling practices, improved hygiene, and environmental sanitation is essential in reducing the burden of Salmonella infection. In addition, routine antibiotic susceptibility surveillance should be prioritized to monitor resistance trends and guide effective treatment strategies.
References
Abdullahi, M. (2010). Incidence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Salmonella species in Children Attending some Hospitals in Kano State, Nigeria. Bayero Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 3(1); 202-206.
Adogo, L., Samuel, G., and Abalaka, M. (2015). Sero-prevalence of Salmonella Typhirium pregnant women in Niger State. Journal of Microbiology Research 5(3); 118-121
Akinyemi K. O, Smith S. I, Oyefulu of Bola A. O, Coker A. O. (2019). Multidrug Resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Isolated from Patients with Typhoid Fever Complications in Lagos, Nigeria. Public Health, 119:321-327
Ameh, I.G., and Opara, W.E.K, (2004), Typhoid; A record of cases in Sokoto, Nigeira. Pakistan Journal of Biological Science 7: 1177-1780
Anchau, Z.G., Olonitola, O.S and Ella. E. E. (2016). Prevalence and Antibiotics Susceptibility of Salmonella species Isolated from Patients Attending Selected Hospitals in Zaria. Scientific journal Microbiology, 5(3):1-6.
Cheesebrough, M. (2010). District Laboratory Characterization of Multiple Antimicrobial Practice in Tropical Countries. Cambridge resistant Salmonella enterica isolated from indigenous vegetables and poultry. University Press, New York, 157-164
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). (2024). M100: Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing (34th ed.).
CLSI. (2024). Breakpoint Implementation Toolkit (BIT): Using current breakpoints in clinical labs.
Gallies, R. R. (2007). Lecture Notes on Medical Microbiology (2nd ed.). New York Black Well Scientific Publication. Pp 220
Ifeanyi, C.I.C., Bassey, E.B., Ikeneche, N.F., Isy, R.N., and Akpa, A.C. (2013). British Microbiological Research Journal, 3(3):431-439.
Ikhimiukor, O. O., Oaikhena, A. O., Afolayan, A. O., Fadeyi, A., Kehinde, A., & Okeke, I. N. (2022). Genomic characterization of invasive typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella in southwestern Nigeria. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 16(8), e0010716.
Imade E, Enagbonma BJ, Isichei-Ukah BO, Igbinosa E. (2024). Curbing the menace of antimicrobial resistance in Nigeria: an integrative review of social action approaches. The Nigerian Health Journal, 2024; 24(2): 1178 – 1188
Inabo H.I, Olonitola S.O and Aminu M (2016). Antibiotic susceptibility of Salmonella Specie Prevalent among children of 0-5years with diarrhea in Katsina State, Nigeria. Arch Med Biomedical Resources, 3:(40)
Laboratory Epidemiology of Salmonella Infections and Multi-Drug Resistance in Nigeria. (2025). medRxiv preprint. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.07.11.25331365v1.full-text?
Lee, D., Chang, H. H., Sarant, S. E., & Levy, K. (2019). Precipitation and salmonellosis Incidence in Georgia, USA: Interactions between Extreme Rainfall Events and Antecedent Rainfall Events Conditions. Environmental Health Perspectives, 127(9).
Maral Rahmani, Seyed Mostafa, Peighambari, Christina Aabysvendsen, Lina M Cavaco Yvonne Agerso and Rene S Henndriksen. (2013). Molecular Clonality and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella enteric Serovars Entritidis and Infantis from Broiler in Three Northern Regions of Iran. BioMed Central Veterinary Research, 9:6.
Mengitsu. G., Mulegeta, G., Lema. T. and Asetta, A (2014). Journal of Microbial and Biochemical Technology.
Montville, T. and Mathews, K. (2008). Food Microbiology: An Introduction (2nd edition), U.S.A: ASM Press, Washington, 122-29
Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC). (2024). Nigeria’s One-Health National Action Plan on AMR (NAP 2.0), 2024–2029 (policy document). Nigeria Centre for Disease Control https://ncdc.gov.ng/themes/common/docs/protocols/353_1729270476.pdf
Osose, E.B., Okafor, C.O.O., Onu, E.N., Ovia K. N., Okoroafor, I., Adie, U.F., Okoh, N.F., Nwachi, A.C., Iroha, I. R. (2025). Multidrug-resistant Salmonella species harboring sulfonamide (sul resistant gene isolated from typhoid patients in a university teaching hospital – A threat to public health. Total Environment Microbiology, 1 (3) 100021.
Subhas, C.P. (2012). Text Book of Microbiology and Immunology 2nd Edition. Reed Elsevier India Private Limited 682PPSwartz, 3, M.N. (2002). Clinical Infectious Diseases, 34:11-12
Van Puyvelde, S., de Block, T., Sridhar, S., Bawn, M., Kingsley, R. A., Ingelbeen, B. (2023). A genomic appraisal of invasive Salmonella Typhimurium and associated antibiotic resistance in sub-Saharan Africa. Nature Communications, 14, 6392. Nature https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-41152-6
Wang, Y., Xu, X., Jia, S., Qu, M., Pei, Y., Gao, G. F. (2025). A global atlas and drivers of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella during 1900–2023. Nature Communications, 16, 4611. Nature https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-59758-3
World Health Organization (WHO) Regional Office for Africa. (2024). Nigeria launches second National Action Plan to combat AMR (news release)
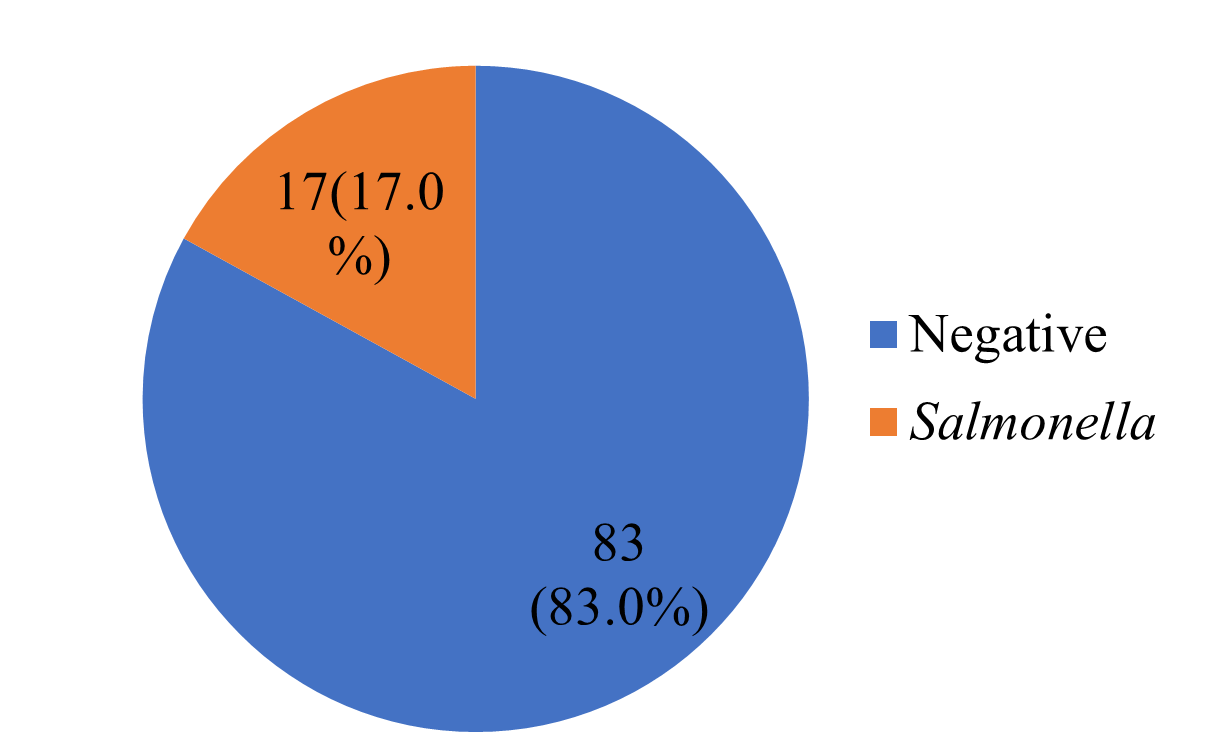
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Science Research and Reviews

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




