Phytochemical and Nutritional Evaluation of Phyllanthus niruri Leaves: Implications for Ethnomedicinal Use
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70882/josrar.2025.v2i5.121Keywords:
Antioxidants, Ethnomedicine, Phyllanthus niruri, Phytochemical screening, Proximate analysisAbstract
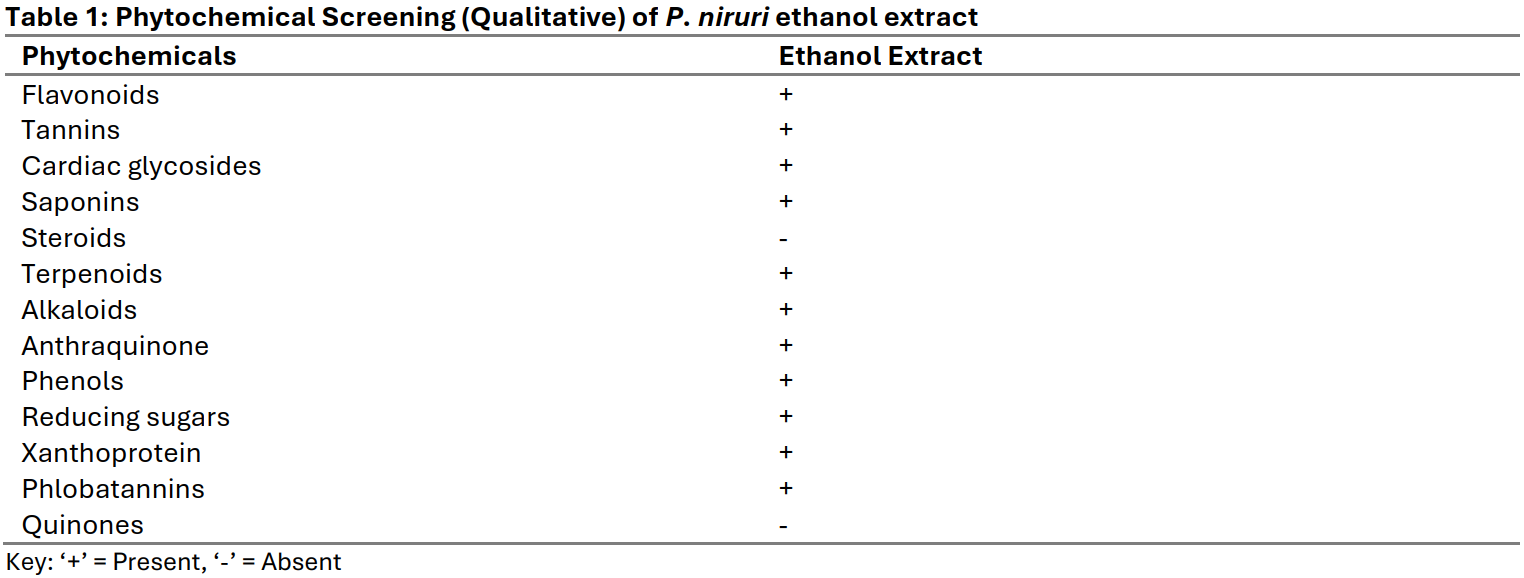
The global resurgence of interest in plant-based therapeutics has intensified scientific efforts toward the identification and validation of medicinal plants as sustainable sources of bioactive compounds. Consequently, a thorough biochemical characterization of such traditional plants is essential to support drug discovery and development. This study investigated the phytochemical composition and proximate profile of the leaves of Phyllanthus niruri (P. niruri), a plant widely recognized in traditional medicine for the management of ailments such as hepatitis, urolithiasis, and diabetes. Fresh P. niruri leaves were extracted using 100% ethanol, and standard analytical procedures were employed for phytochemical and proximate analyses. The phytochemical screening indicated a rich presence of key secondary metabolites, including flavonoids, saponins, tannins, alkaloids, phenols, terpenoids, cardiac glycosides, anthraquinones, and phlobatannins, whereas steroids and quinones were absent. Proximate analysis revealed a high moisture content (39.33 ± 0.48%) and appreciable levels of carbohydrates (31.47 ± 0.58%) and crude fibre (15.26 ± 0.37%), alongside moderate quantities of crude fat (6.60 ± 0.57%), total ash (8.60 ± 0.28%), and crude protein (2.35 ± 0.17%). The abundance of polyphenolic compounds (phenols, tannins, flavonoids) and alkaloids suggests a biochemical basis for the plant’s reported antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral activities. Additionally, its considerable fibre and carbohydrate contents indicate potential value as a dietary supplement. Overall, these findings substantiate the ethnopharmacological relevance of P. niruri, reinforcing its potential as a nutraceutical resource and promising candidate for future drug development.
References
Agostoni, C., Bresson, J. L., Fairweather Tait, S., Flynn, A., Golly, I., Korhonen, H., Lagiou, P., Løvik, M., Marchelli, R., and Martin, A. (2012). Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for protein: EFSA panel on dietetic products, nutrition and allergies (NDA). EFSA JOURNAL, 10(2), 1-66.
Al-Gbouri, N., and Hamzah, A. (2018). Evaluation of Phyllanthus emblica extract as antibacterial and antibiofilm against biofilm formation bacteria. Iraqi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 49(1).
Bagalkotkar, G., Sagineedu, S., Saad, M., and Stanslas, J. (2006). Phytochemicals from P. niruri Linn. and their pharmacological properties: a review. Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology, 58(12), 1559-1570.
Cheema, H. S., and Singh, M. P. (2021). The use of medicinal plants in digestive system related disorders—a systematic review. J. Ayurvedic Herb. Med, 7(3), 182-187.
Chemists, A. o. O. A. (2000). Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (Vol. 11). The Association.
Chemists, A. o. O. A., and Chemists, A. o. O. A. (1920). Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (Vol. 2). Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
Chen, Z., and Zhang, R. (2023). Suppressed effects of Phyllanthus urinaria L. ethyl acetate extract on hepatitis B virus both in vitro and in vivo. Precis. Med. Res, 5(3), 15.
Edeoga, H. O., Okwu, D., and Mbaebie, B. (2005). Phytochemical constituents of some Nigerian medicinal plants. African Journal of Biotechnology, 4(7), 685-688.
Finar, G. (1986). Plants of economic importance. Medicinal Plants and Medicine in Africa. Spectrum Books Ltd. Ibadan, 78, 150-153.
Harborne, A. (1998). Phytochemical methods a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. springer science and business media.
Harborne, J. B. (1976). A unique pattern of anthocyanins in Daucus carota and other Umbelliferae. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 4(1), 31-35.
Harikrishnan, H., Jantan, I., Alagan, A., and Haque, M. A. (2020). Modulation of cell signaling pathways by Phyllanthus amarus and its major constituents: potential role in the prevention and treatment of inflammation and cancer. Inflammopharmacology, 28(1), 1-18.
Harikrishnan, H., Jantan, I., Haque, M. A., and Kumolosasi, E. (2018). Phyllanthin from Phyllanthus amarus inhibits LPS‐induced proinflammatory responses in U937 macrophages via downregulation of NF‐κB/MAPK/PI3K‐Akt signaling pathways. Phytotherapy Research, 32(12), 2510-2519.
Harish, R., and Shivanandappa, T. (2006). Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective potential of Phyllanthus niruri. Food chemistry, 95(2), 180-185.
Khadka, B. (2021). Effect of Herbal Extract on the Shelf Life of Paneer Department of Food Technology Central Campus of Technology Institute of …].
Khan, V., Najmi, A. K., Akhtar, M., Aqil, M., Mujeeb, M., and Pillai, K. (2012). A pharmacological appraisal of medicinal plants with antidiabetic potential. Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied sciences, 4(1), 27-42.
Kiemer, A. K., Hartung, T., Huber, C., and Vollmar, A. M. (2003). Phyllanthus amarus has anti-inflammatory potential by inhibition of iNOS, COX-2, and cytokines via the NF-κB pathway. Journal of Hepatology, 38(3), 289-297.
Kumar, B., Kumar, S., and Madhusudanan, K. (2020). Phytochemistry of Plants of Genus Phyllanthus. CRC Press.
Kumar, K., and Kuttan, R. (2005). Chemoprotective activity of an extract of Phyllanthus amarus against cyclophosphamide induced toxicity in mice. Phytomedicine, 12(6-7), 494-500.
Kumara, K. S., Shishupala, S., and Prakash, H. (2023). The genus Phyllanthus: A rich source of pharmacologically active compounds useful in traditional and modern medicines. In Ethnic Knowledge and Perspectives of Medicinal Plants (pp. 245-273). Apple Academic Press.
Mahmood, S. U., Bashir, M. H., Idrees, A., Abrar, M., Qadir, Z. A., Mao, R., and Fang, X. (2024). Nutritional Evaluation of Wheat (Triticum aestivum: Poaceae) Varieties Infested with Rhizoglyhphus tritici (Acari: Acaridae). Systematic and Applied Acarology, 29(12), 1728-1741.
Malik, D., Narayanasamy, N., Pratyusha, V., Thakur, J., and Sinha, N. (2023). Inorganic nutrients: macrominerals. In Textbook of Nutritional Biochemistry (pp. 391-446). Springer.
Mavi, A., Terzi, Z., Özgen, U., Yildirim, A., and Coşkun, M. (2004). Antioxidant properties of some medicinal plants: Prangos ferulacea (Apiaceae), Sedum sempervivoides (Crassulaceae), malva neglecta (malvaceae), Cruciata taurica (Rubiaceae), Rosa pimpinellifolia (Rosaceae), Galium verum subsp. verum (Rubiaceae), urtica dioica (urticaceae). Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 27(5), 702-705.
Nielsen, F. H. (2010). 12 Macromineral Nutrition.
Nisar, M. F., He, J., Ahmed, A., Yang, Y., Li, M., and Wan, C. (2018). Chemical components and biological activities of the genus Phyllanthus: A review of the recent literature. Molecules, 23(10), 2567.
Obadoni, B., and Ochuko, P. (2002). Phytochemical studies and comparative efficacy of the crude extracts of some haemostatic plants in Edo and Delta States of Nigeria. Global Journal of pure and applied sciences, 8(2), 203-208.
Ojo, O. A., Ogunlakin, A. D., Gyebi, G. A., Ayokunle, D. I., Odugbemi, A. I., Babatunde, D. E., Akintunde, E. A., Ezea, S. C., Asogwa, N. T., and Asaleye, R. M. (2025). Profiling the antidiabetic potential of GC–MS compounds identified from the methanolic extract of Spilanthes filicaulis: Experimental and computational insight. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 43(3), 1392-1413.
Omoregie, E. S., and Oikeh, E. I. (2015). Comparative studies on the phytochemical composition, phenolic content and antioxidant activities of methanol leaf extracts of Spondias mombin and Polyathia longifolia. Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences, 8(2), 145-149.
Patel, J. R., Tripathi, P., Sharma, V., Chauhan, N. S., and Dixit, V. K. (2011). Phyllanthus amarus: ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology: a review. Journal of ethnopharmacology, 138(2), 286-313.
Prananda, A. T., Dalimunthe, A., Harahap, U., Simanjuntak, Y., Peronika, E., Karosekali, N. E., Hasibuan, P. A. Z., Syahputra, R. A., Situmorang, P. C., and Nurkolis, F. (2023). Phyllanthus emblica: a comprehensive review of its phytochemical composition and pharmacological properties. Frontiers in pharmacology, 14, 1288618.
Pratima, H., Shiraguppi, A., Joojagar, P., Shah, K., Cheeraladinni, S. S., Singh, P. S., Mendem, S. k., and Chauhan, N. S. (2025). Phytochemical profile and hepatoprotective potentiality of Phyllanthus genus: a review. Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology, 77(2), 189-205.
putrescentiae Schrank, T. (2014). Quantitative and qualitative losses due to Tyrophagus putrescentiae Schrank (Acari: Acaridae) in wheat and its management Haryana Agricultural University Hisar].
Rastogi, R. (1991). Mehrotra. BN Compendium of Indian Medicinal Plants. CDRI, Lucknow and Institute of Science Communication, New Delhi, 2, 215.
Shrivastava, S. K., and Dwivedi, S. (2020). Insights into the natural hypoglycemic principles: Translating traditional molecular target knowledge into modern therapy. In Biochemistry, Biophysics, and Molecular Chemistry (pp. 251-283). Apple Academic Press.
Simeon, E. O., Amamilom, N. S., and Azuka, I. W. (2018). Metal assessment and phytochemical screening of orange fruit (Citrus sinensis) seeds and peels. J Pharmacogn Phytochem, 7(3), 709-714.
Singh, M. P., and Panda, H. (2005). Medicinal herbs with their formulations. Daya Books.
Sofowora, A. (1996). Research on medicinal plants and traditional medicine in Africa. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 2(3), 365-372.
Taylor, L. (2003). Technical Data Report for Chancap Piedra Stone Breaker (Phyllanthus niruri). Herbal Secrets of the Rainforest, 2nd edition, London, Sage Press, Inc.
Thuy, N. T. N., Ha, P. T., Thao, N. T. P., Nhan, V. D., Bang, T. H., Pham, D. T., and Thuy, B. T. P. (2025). Therapeutic potential of Phyllanthus spp. in sustainable aquaculture: a phytopharmacological perspective. RSC Advances, 15(49), 41432-41446.
Trease, G., and Evans, W. (1978). Pharmacology, 11th. Bailliere Tindall Ltd., London, 60-75.
Tungmunnithum, D., Thongboonyou, A., Pholboon, A., and Yangsabai, A. (2018). Flavonoids and other phenolic compounds from medicinal plants for pharmaceutical and medical aspects: An overview. Medicines, 5(3), 93.
Upadhyay, R., and Tiwari, K. N. (2023). The antiviral potential of Phyllanthus species: a systematic review. Archives of virology, 168(7), 177.
Valletta, A., Iozia, L. M., Fattorini, L., and Leonelli, F. (2023). Rice phytoalexins: half a century of amazing discoveries; part I: distribution, biosynthesis, chemical synthesis, and biological activities. Plants, 12(2), 260.
World Health Organization. (2002). WHO traditional medicine strategy 2002-2005. In WHO traditional medicine strategy 2002-2005 (pp. 61-61).
Williams, R. J., Spencer, J. P., and Rice-Evans, C. (2004). Flavonoids: antioxidants or signalling molecules? Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 36(7), 838-849.
Wink, M. (2015). Modes of action of herbal medicines and plant secondary metabolites. Medicines, 2(3), 251-286.
Wu, Y., Lu, Y., Li, S.-y., Song, Y.-h., Hao, Y., and Wang, Q. (2015). Extract from Phyllanthus urinaria L. inhibits hepatitis B virus replication and expression in hepatitis B virus transfection model in vitro. Chinese journal of integrative medicine, 21(12), 938-943.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Science Research and Reviews

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




