Integrated Phytochemical and Hematological Assessment of Hydroethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia carnea in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70882/josrar.2025.v2i5.115Keywords:
Diabetes, Haematological indices, Justicia carnea, Phytochemical compositionAbstract
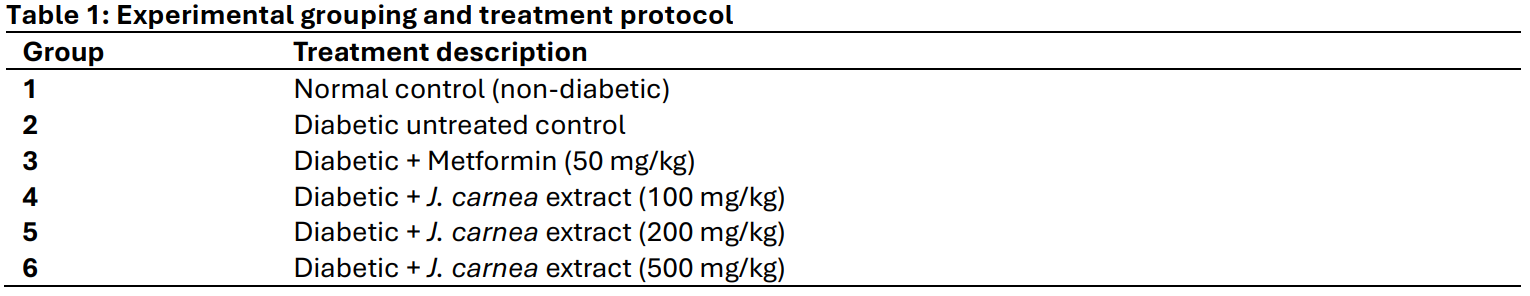
Diabetes mellitus, a multifactorial metabolic disorder, is often associated with hematological and oxidative alterations that contribute to disease complications. This study investigated the phytochemical composition and biochemical effects of the hydroethanolic leaf extract of Justicia carnea on hematological parameters in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Thirty-six (36) male albino Wistar rats were divided into six groups (n = 6). Diabetes was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (50 mg/kg), except in the normal control group. The diabetic control group received no treatment, while the reference group received metformin (50 mg/kg). Test groups were orally administered Justicia carnea hydroethanolic extract at doses of 100, 200, and 500 mg/kg daily for 28 days. Acute toxicity was assessed using Lorke’s method. At the end of the experiment, fasting blood glucose levels were measured, and blood samples were collected via cardiac puncture for hematological analysis. Phytochemical screening revealed the presence of flavonoids, phenols, steroids, tannins, and terpenoids, indicating significant bioactive potential. Proximate analysis showed high carbohydrate (50.91 %) and moisture (21.11 %) content, with lower levels of crude fat (0.25 %) and protein (1.25 %). Treatment with Justicia carnea extract produced a dose-dependent improvement in hematological indices, including red blood cell count, hemoglobin concentration, and white blood cells, compared with diabetic controls. These effects suggest a restorative influence on hematopoietic function, potentially mediated by phytochemical constituents with antioxidant or cytoprotective activity. These findings suggest that Justicia carnea may possess hematoprotective and restorative properties beneficial in the management of diabetes-induced hematological alterations.
References
Aboonabi, A., Rahmat, A., Fauziah, O.F. (2014). ‘Antioxidant effect of pomegranate against streptozotocin-nicotinamide generated oxidative stress-induced diabetic rats’, Toxicology Reports. 1, pp. 915-922.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.10.022
Adeloye, D., Ige, J.O., Aderemi, A.V., Adeleye, N., Amoo, E.O., Auta, A. et al. (2017) ‘Estimating the prevalence, hospitalisation and mortality from type 2 diabetes mellitus in Nigeria: A systematic review and meta-analysis’, BMC Public Health, 17(1), pp 1249. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-5130-6
Adesokan, A.A. and Akanji, M.A(2011). ‘Antidiabetic potential of Justicia carnea leaves extract in alloxan-induced diabetic rats’, African Journal of Biochemistry Research, 5(8), pp 252–256.Available at: https://academicjournals.org/journal/AJBR/articleabstract/5C982B812861
Ajibesin, K.K., Ekpo, B.A., Bala, D.N., Essien, E.E., Adesanya, S.A., 2008. Ethnobotanical survey of Akwa Ibom State of Nigeria. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 115(3), 387–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.021
Akintimehin, E.S., Adeyemi, O.S., Olayemi, F.O., Odu, O.O., 2021. Safety assessment of oral administration of ethanol extract of Justicia carnea in Wistar rats. Clinical Phytoscience 7, 61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-020-00234-4
Anarado, C.E., Ajiwe, V.I.E., Anarado, C.J.O., Obumselu, O.F., Umedum, N.L. and Okafor, S.E. (2021). The phytochemistry, ethnomedicinal and pharmacology uses of Justicia carnea Lindl used in traditional medicine in Nigeria—A review. South Asian Research Journal of Natural Products, 4(4), pp 85–93. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356749503
Anyasor, G.N., Okanlawon, A.A., Ogunbiyi, B., 2019. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of Justicia secunda Vahl leaf extract using in vitro and in vivo inflammation models. Clinical Phytoscience 5, 49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-019-0137-8
AOAC, (2000). Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 14th Ed. Washington D.C. USA.
AOAC. (1990). Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Vol. II, 15th ed. Sec.985.29. The Association: Arlington, VA.
Asante-Kwatia, E., Adosraku, R.K., Woode, E., Antwi, D.A., 2023. A study on Justicia flava (Forssk.) Vahl: Pharmacognostic, phytochemical and pharmacological investigations. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2023, Article ID 9133288. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/9133288
Asogwa, N.T., Akindele, A.J, Orish, C.N., et al. (2020). ‘Proximate, phytochemical and Mineral composition of Justicia carnea leaves’, J Med Plants Stud, 8(3), pp 57–61.
Ayoola, P.B. and Adeyeye, A. (2009). ‘Proximate analysis and nutrient evaluation of some Nigerian leafy vegetables’, Afr J Food Sci, 3(9), pp 299–302.
Balasundram, N., Sundram, K., and Samman, S. (2006). ‘Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: Antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses’, Food Chemistry, 99(1), pp 191–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.042
Berger, A., Jones, P.J.H. and Abumweis, S.S. (2004). ‘Plant sterols: Factors affecting their efficacy and safety as functional food ingredients’, Lipids in Health and Disease, 3(1), pp 5-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-3-5
Bouttwell, R.K. (1988). ‘Dietary fibre in health and disease’, Am J Clin Nutr, 47(5), pp 975–983.
Corrêa, G.M. and Alcântara, A.F. (2012). ‘Chemical constituents and biological activities of species of Justicia’, Journal of Pharmacognosy, 22(1), pp 220–238.
Cosme, F., Aires, A., Pinto, T., Oliveira, I., Vilela, A. and Gonçalves, B. (2025). A comprehensive review of bioactive tannins in foods and beverages: Functional properties, health benefits, and sensory qualities’. Molecules, 30(4), pp 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040800
Davidson MH, Maki KC, Karp SK. Effects of dietary fibre on plasma lipids. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 1995;1(1):30–35.
Diallo, A., Gbéassor, M., Vovor, A., Eklu-Gadegbeku, K., Aklikokou, K., Agbonon, A., Abena, A. A., de Souza, C. and Akpagana, K. (2008). ‘Effect of Tectona grandis on phenylhydrazine-induced anaemia in rats’, Fitoterapia, 79(5), pp 332–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2008.02.005
Eaton, D.L. and Klaassen, C.D. (2001). Principle of Toxicology, in Klassen CD (ed) Casaret and Doll’s Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 6th McGraw-Hill, pp 11 – 13.
Edeoga, H. O., Okwu, D. E., and Mbaebie, B. O. (2005). Phytochemical constituents of some Nigerian medicinal plants. African journal of biotechnology, 4(7), 685-688.
Edem, D.O.(2020) Effects of Tapinanthus globiferus leaf extract on blood glucose and pancreatic histology in alloxanized and nonglycaemic rats: Archives of Diabetes and Endocrine System. 2020;3(2): 34-43.
Eluhike, N. and Onoagbe, I.(2018). ‘Changes in organ and body weight, serum amylase and antidiabetic effects of tannins on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats’, Journal of Insulin Resistance, 3(1), pp 1-2.
Etame, R.M.E., Mouokeu, R.S., Poundeu, F.S.M., Voukeng, I., Cidjeu, C.L.P., Tiabou, A.T., Yaya, A.J.G., Ngane, R.A N., Kuiate, J.R., and Etoa, F.X. (2019). ‘Effect of fractioning on antibacterial activity of n-butanol fraction from Enantia chlorantha stem bark methanol extract’, BMC Complement Altern Med, 19(1), pp. 56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2459-y10.1186/s12906-019-2459-y
FAO , (1990).Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Dietary Fibre in Human Nutrition: Report of an Expert Consultation. Rome: FAO; 1990.
Finar, G. (1986). ‘Plants of economic importance’. Medicinal Plants and Medicine in Africa. Spectrum Books Ltd. Ibadan, 78, pp 150-153.
Harborne, J.B. (1998). ‘Phytochemical methods: A guide to modern techniques of plant analysis (3rd ed.). Chapman and Hall, pp 33-38
IDF International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas (10th ed.). International Diabetes Federation. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/
Lenzen, S. (2019). ‘The mechanisms of alloxan and streptozotocin-induced diabetes’, Diabetologia, 51(2), pp:216-257.
Lombe, B.K., Mpondo, M.E., Tshibangu, D.S.T., Mpiana, P.T. (2017). ‘Ethnobotanical and ethnopharmacological survey of Justicia species used in the Democratic Republic of Congo for the management of inflammatory and infectious diseases’, Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 6(3), pp 2432. Available at: https://www.phytojournal.com/archives/2017/vol6issue3/PartA/6-2-130.pdf
Lorke, D. (1983). ‘A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing’, Archives of Toxicology, 54(4), pp 275–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01234480
McDonald, P., Edwards, R.A., Greenhalgh, J.G. and Morgan, C.A. (1998). Animal Nutrition. 5th ed. Essex: Longman Scientific and Technical
Medapa, S., Singh. G.R. and Ravikumar, V. (2015). ‘The photochemical and antioxidant screening of justicia wyna-adensis’, African Journal of Plant Sciences, 5(9), pp 489-492.
Michelle C, Lang T, Edelman P. Role of lipids in cell membrane structure and function. J Nutr Biochem. 1993;4(3):123–130.
Musa, A.Z., Umar, I., Obiagwu, P.N.and Ibrahim, M. (2024) Prediabetes in children and adolescents: a narrative review’, Ann Afr Med Res, 7, pp:486. doi:10.4081/aamr.2024.486.
National Research Council. (2011). Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Eighth Edition. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/12910
Obadoni, B.O. and Ochuko, P.O. (2001). ‘Phytochemical studies and Comparative efficacy of the crude extracts of some homeostatic plants in Edo and Delta States of Nigeria’, Global J Pure Appl Sci, 8, pp 203-208.
Oboma, Y.I., Beredugo, S.B., Nyenke, C., Bot, Y.S., Idehen, C.I., Ikiomoye, L.B. (2024). ‘Therapeutic and toxicological assessment of hydroethanolic leaf extracts of Jatropha curcas and Justicia carnea in apparently healthy Sprague Dawley rats’, Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 17(10),317-328. https://doi.org/10.62347/SYZP2468.
Ogbe, R.J., Adoga, G.I. and Abu, A.H. (2010). ‘Antianaemic potentials of some plant extracts on phenylhydrazine-induced anaemia in rabbits’, Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 4(8), pp. 680–684.
Ojeaburu, S.I., Eimoga, N. (2024). ‘Attenuation of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Hepatorenal Damage by Methanol Extract of Justicia carnea Leaves in Male Wistar Rats’, Bulletins of Natural and Applied Sciences, 1(3), pp 18-33. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14189695
Ojeaburu, S.I., Olasehinde, O. (2025). ‘Enantia chlorantha Stem Back Extracts Enhances Haematological Indices in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats’, Journal of Science Research and Reviews, 2(3), pp 137-145. https://doi.org/10.70882/josrar.2025.v2i3.101
Ojo, O., Njanje, I., Abdissa, D., Swart, T., Higgitt, R. L. and Dorrington, R. A. (2025). ‘Newly isolated terpenoids (covering 2019–2024) from Aspergillus species and their potential for the discovery of novel antimicrobials’. Natural Products and Bioprospecting, 15(1), pp. 19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-025-00501-2
Okeke, C.U. and Elekwa, I. (2006) ‘Proximate and preliminary phytochemical analysis of Avocado (Persea americana) leaves’, J Med Plants Res, 2(3), pp. 25–28.
Okeke, C.U., Iweala, E.E.J., Ezeonu, F.C.(2008). ‘Nutritional evaluation of some Nigerian traditional soups’, J Biol Sci, 8(1), pp.131–134.
Onoja, S.O., Ezeja, M.I., Omeh, Y.N., Onwukwe, B.C. (2017). ‘Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of methanolic extract of Justicia secunda Vahl leaf’, Alexandria Journal of Medicine, 53(2), pp. 207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2016.06.001
Onyeyili, P. A., Egwu, G. O., Jibike, G. I., Pepple, D. J. and Ohaegbulam, J. O. (2013). ‘Seasonal variation in haematological indices in the grey-breasted guinea fowl’. Nigeria Journal of Animal Production, 12(2), pp.108-110.
Oso, B. J., Oyewo, E. B. and Oladiji, A. T. (2019). ‘Influence of ethanolic extracts of dried fruit of Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) rich on haematological and biochemical parameters in Wistar rats’, Clinical Phytoscience, 5, Article 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-019-0104-4.
Panche, A.N., Diwan, A.D., and Chandra, S.R. (2016). ‘Flavonoids: An Overview’ Journal of Nutritional Science, 5, pp. e47. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2016.41
Qamar, F., Sultana, S., and Sharma, M. (2023). ‘Animal models for the induction of diabetes and its complications’, J Diabetes Metab Disord, 22(2), pp. 1021-1028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-
Qin, W., Wu, Y., Liu, J., Yuan, X., and Gao, J. (2022). ‘A Comprehensive Review of the Application of Nanoparticles in Diabetic Wound Healing: Therapeutic Potential and Future Perspectives’, Int J Nanomedicine, 17, pp.6007-6029. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S386585
Radhika, J., Sathaya, .S. and Jothi, G. (2013). Cardioprotective role of Justicia traquebareinsis leaf extract and Justicia carnea leaf extract in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in albino rats. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 3(4), pp. 124-128.
Rahmani, A. H., Alsahli, M. A., Khan, A. A. and Almatroodi, S. A. (2023). ‘Quercetin, a Plant Flavonol Attenuates Diabetic Complications, Renal Tissue Damage, Renal Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats’, Metabolites, 13(1), pp.130. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010130 10.3390/metabo13010130
Raven, P.H. and Evert, R.F. (1999). Eichhorn SE. Biology of Plants. 6th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman;
Rhee, S. Y. and Kim, Y. S. (2018). ‘The role of advanced glycation end products in diabetic vascular complications’, Diabetes & Metabolism Journal, 42(3), pp.188-195. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0105 PMC+2PubMed+2
Roy, A., Khan, A., Ahmad, I., Alghamdi, S., Rajab, B.S., Babalghith, A.O., Alshahrani, M.Y., Islam, S. and Islam, M.R. (2022). ‘Flavonoids a Bioactive Compound from Medicinal Plants and Its Therapeutic Applications’, Biomed Res Int, 6, pp. 5445291. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5445291.
SACN (Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition). (2018). ‘Carbohydrates and Health’, London: Public Health England.
Saeedi, P., Petersohn, I., Salpea, P., Malanda, B., Karuranga, S., Unwin, N. et al. (2019). ‘Global and diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045’, Diabetes Researchand Clinical Practice, 157,pp.107843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
Singh V.P., Bali A., Singh N., Jaggi A.S. (2014). ‘Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetic Complications’, The Korean Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 18(1), pp. 1-14. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2014.18
Soetan, K.O. and Oyewole, O.E. (2009). ‘The need for adequate processing to reduce the anti-nutritional factors in plants used as human foods and animal feeds: A review’, African Journal of Food Science, 3(9), pp. 223-231.
Sofowora, A. (1996). ‘Research on medicinal plants and traditional medicine in Africa’, The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 2(3), pp. 365-372.
Świątek, Ł., Flisiński, M., Grabarczyk, Ł. and Kamil, R. (2023). ‘Chemical characterization of different extracts of Justicia secunda Vahl., a traditional medicinal plant in tropical regions including West Africa’, Antioxidants 12(2), pp. 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020509
Teo K, Adeoye O, Ogunlana O, Shen M, Lau E, Wu Y. et al. (2024). ‘Global, regional, and national trends in type 2 diabetes mellitus burden among adolescents and young adults aged 10-24 years from 1990 to 2021: a trend analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study’ World J Pediatr, 21(1),pp.73-89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-024-00861-8.
Vunchi, M.A., Umar, A.N., King, M.A., Liman, A.A., Jeremiah, G., Aigbe, C.N. (2011). ‘Proximate, vitamins and mineral composition of Vitex doniana (black plum) fruit pulp’, Nig J Basic Appl Sci,19(1), pp. 97–101.
WHO. (2013) World Health Organization Traditional Medicine Strategy 2014–2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
Xie, L., Xu, F., Liu, S., Ji, Y., Zhou, Q., Wu, Q. and Xie, P. (2013). ‘Age- and Sex-Based Hematological and Biochemical Parameters for Macaca fascicularis’. PLoS ONE, 8(6), pp.44-68.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Science Research and Reviews

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




