Chemical Speciation, Bioavailability and Multi-Index Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Dumpsite-Affected Farmland Soils of Anyigba, Nigeria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70882/josrar.2025.v2i5.113Keywords:
Agricultural Soils, Dumpsites, Heavy Metals, Ecological Risk, Pollution Index, Soil propertiesAbstract
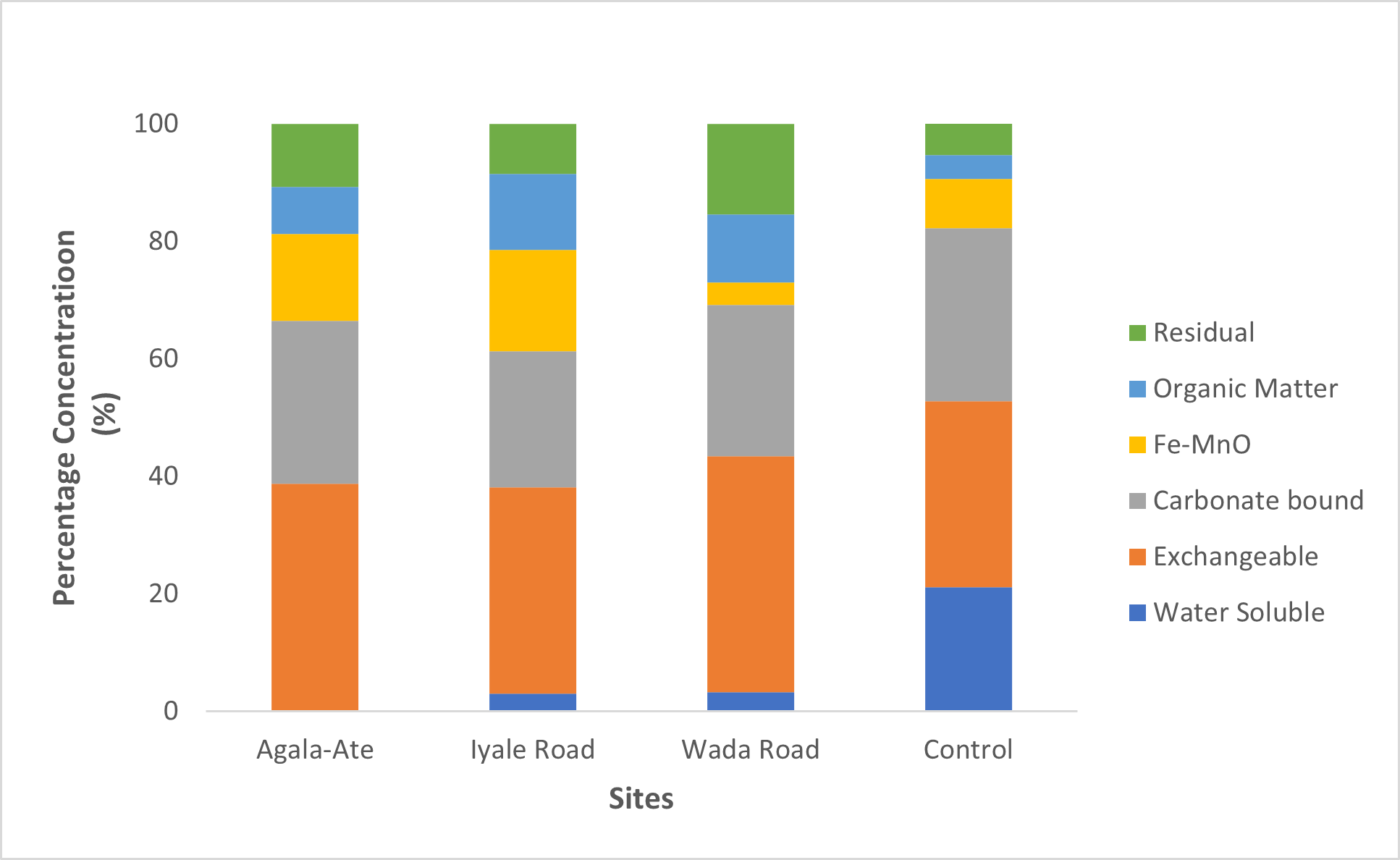
This study assessed the physicochemical properties, chemical speciation, and ecological risk of heavy metals in farmland soils near municipal dumpsites in Anyigba, Nigeria. The soils were slightly acidic (pH 5.2–6.4), with moderate organic matter (1.82–2.65%) and cation exchange capacity (7.4–12.3 cmol/kg), while electrical conductivity was low (92–148 µS/cm), indicating non-saline conditions that promote metal mobility. Heavy metals occurred in the ranges: Cd (4.60–5.91 mg/kg), Cu (5.81–12.44 mg/kg), Ni (11.70–18.92 mg/kg), Cr (4.93–8.17 mg/kg), and Pb (3.99–6.25 mg/kg). Speciation analysis showed Cd concentrated in exchangeable and carbonate fractions (45–58%), reflecting high mobility; Cu was mainly bound to organic matter (40–52%); Ni dominated reducible fractions (35–48%); Cr occurred in the residual fraction (55–68%); and Pb partitioned into carbonate and reducible fractions (30–45%). Contamination factors (CF) indicated very high Cd contamination (6.0–7.5), moderate Ni (2.0–3.0), Cu (1.2–2.1), and Pb (1.1–1.8), and low Cr (0.8–1.4). The Pollution Load Index (PLI) ranged 1.2–2.0, confirming overall deterioration, while the Nemerow Pollution Index (NPI) of 2.4–3.1 signaled considerable pollution risk. Ecological Risk Index (ERI) values highlighted Cd as the major contributor (60–70% of total risk), with individual ERI of 180–220, categorizing it as a “considerable ecological risk.” In contrast, Cu, Ni, Cr, and Pb presented low to moderate risks (ERI < 40). Integration of soil properties with speciation data indicated that acidic pH and relatively low organic matter enhanced Cd solubility and bioavailability, whereas organic complexation stabilized Cu. These results demonstrate that ecological assessments must consider both total concentrations and chemical forms of metals. Recommended interventions include phytoremediation, soil organic amendments, and stricter waste management to mitigate contamination and ensure sustainable agriculture in Anyigba.
References
Abata, E. O., Adunbi, J. O., Babaniyi, B. R., & Ajayi, O. O. (2024). Heavy metal content in dumpsite soils and vegetables: A case study of Ondo Town, Nigeria. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 19(1), 97–104. https://doi.org/10.30574/gscarr.2024.19.1.097
Abbas, T., Yousaf, B., Ali, M. U., Munir, M. A. M., & Ahmad, A. (2023). Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in urban and peri-urban soils: Application of ecological risk index (ERI) and geo-accumulation index (Igeo). Environmental Pollution, 316, 120481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120481
Abiola, O. A., Akinola, M. O., & Adesuyi, A. A. (2021). Assessment of heavy metal contamination and ecological risk using contamination factor and pollution load index in soils around dumpsites in Lagos, Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(6), 345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09065-7
Adesina, G. O., Oladejo, O. S., & Ajayi, O. O. (2022). Assessment of heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in soils around municipal dumpsites in Southwestern Nigeria. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 18, 100706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100706
Adewumi, A. J., Olatunji, O. S., & Akinola, M. O. (2022). Contamination factor and pollution load index as tools for assessing heavy metal pollution in soils around dumpsites in Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(2), 145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09801-7
Adeyemi, A. O., Oyekunle, J. A. O., & Olutona, G. O. (2023). Fractionation and ecological risk assessment of lead and other heavy metals in urban soils of southwestern Nigeria. Environmental Pollution, 316, 120742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120742
Ahmed, M., Zhou, Y., & Wang, S. (2023). Chemical speciation and potential mobility of copper and zinc in soils near municipal waste disposal sites. Environmental Pollution, 317, 120768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120768
Aikpokpodion, P. E., & Odoemena, C. S. (2022). Soil pH and organic matter as key regulators of heavy metal dynamics in waste-impacted agricultural soils of Southern Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(11), 755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10326-2
Ajibade, T. F., Oladipo, M. O. A., & Yusuf, K. A. (2022). Assessment of heavy metal contamination and ecological risks in agricultural soils impacted by municipal solid waste in Nigeria. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 18, 100690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100690
Alhassan, H., Suleiman, I., & Musa, S. (2023). Influence of soil texture and organic matter on heavy metal retention near municipal dumpsites in Northern Nigeria. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 23(5), 2143–2158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03471-0
Ali, S., Zhang, Q., & Khan, M. (2021). Contamination factor and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around industrial areas. Chemosphere, 263, 128339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128339
Antonangelo, J. A., and Adeoye, G. O. (2024). Comparative evaluation of soil cation exchange capacity using ammonium acetate and compulsive exchange methods. Frontiers in Soil Science, 3, 1371777. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoil.2024.1371777
Arshad, M. A. and Ibrahim, M. (2022). Comparative assessment of gravimetric and dielectric methods for determining soil moisture in tropical regions. Sustainability, 14(18), 11538. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811538
Chatziparaschis, A., Ahmad, F., and Lee, J. H. (2023). Integration of proximal sensors and AI for monitoring soil salinity and conductivity. Applied Biological Chemistry, 66(2), 105–115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13765-023-00849-4
Chen, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, J., & Zhang, H. (2022). Chemical speciation and mobility of lead in contaminated soils: Influence of carbonate, organic matter, and Fe–Mn oxides. Chemosphere, 293, 133624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133624
Chukwu, U. J., Nwankwoala, H. O., & Iwuoha, G. N. (2023). Enrichment factor and ecological risk index of heavy metals in soils around waste dumpsites in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Environmental Challenges, 11, 100759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2022.100759
de Souza, V. B., Hollas, C. E., Bortoli, M., Manosso, F. C., & de Souza, D. Z. (2023). Heavy metal contamination in soils of a decommissioned landfill southern Brazil: Ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere, 339, 139689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139689
Droz, B., Tercier-Waeber, M.-L., and Keller, C. (2021). Copper content and export in European vineyard soils: Influence of fungicide use. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(24), 16228–16238. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c02093
El-Hassanin, A. S. (2022). Chemical fractionation of some heavy metals in soils illegally irrigated with contaminated water. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 44(9), 3341–3356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01113-9
Eze, C. N., Okeke, I. C., & Nnaji, J. C. (2022). Physicochemical properties of soils around dumpsites and their influence on cadmium and lead mobility. Environmental Challenges, 8, 100514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2022.100514
Eze, J. C., & Chukwu, A. (2023). Influence of soil texture on heavy metal accumulation in contaminated soils of southeastern Nigeria. Journal of Soil Science and Environmental Management, 14(2), 33–41. https://doi.org/10.5897/JSSEM2023.0962
Fosu-Mensah, B. Y., & Mensah, A. K. (2021). Soil moisture and pH effects on mobility of zinc, copper, and nickel in Ghanaian landfill soils. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 22, 101409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101409
Fulke, A. B., Ratanpal, S., & Sonker, S. (2024). Understanding heavy metal toxicity: Implications on human health, marine ecosystems, and bioremediation strategies. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 206, 116707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116707
Hassan, M., Khan, A., & Li, X. (2023). Organic carbon-mediated stabilization of heavy metals in agricultural soils impacted by waste disposal. Chemosphere, 333, 138906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138906
Huang, Y., Li, J., & Wang, X. (2022). Application of contamination factor and geo-accumulation index in evaluating soil heavy metal pollution in peri-urban farmlands. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 237, 113547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113547
Huang, Y., Li, Z., Zhang, J., & Chen, H. (2022). Fractionation and bioavailability of copper in contaminated soils: Roles of organic matter and Fe–Mn oxides. Chemosphere, 293, 133575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133575
Ibrahim, T. A., Olanrewaju, R. F., & Adetunji, A. T. (2024). Variability of cation exchange capacity and its role in heavy metal immobilization across soils of Southwestern Nigeria. Scientific African, 16, e01872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2024.e01872
Kakpu, O. J., Okoye, P. A. C., & Onuegbu, T. U. (2024). Chemical fractionation and mobility factor of some heavy metals in refuse dumpsite soil in Awka Metropolis, Anambra State, Nigeria. Chemical Reports, 5(1), 268–274. https://doi.org/10.25082/CR.2024.01.001
Khumalo, N., and Moodley, M. (2023). Evaluation of soil organic carbon dynamics in relation to trace metal retention in amended soils. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11592-2
Kilinc, M., & Orhan, Y. (2025). Improved hydrometer-based soil texture analysis using machine learning correction for ionic interferences. Soil and Tillage Research, 230, 105062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2024.105062
Kubier, A., Wilkin, R. T., & Pichler, T. (2019). Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Applied Geochemistry, 108, 104388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104388
Kumar, S., Singh, R., Pandey, R., & Sharma, K. (2022). Nickel is an essential micronutrient but toxic in excess: A plant physiological perspective. Environmental Pollution, 294, Article 118528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118528
Labidi, O., & Abdelly, C. (2024). Impact of nickel toxicity on growth, fruit quality and chlorosis in plants. Plants, 13(17), 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172361
Landrigan, P. J., Fuller, R., & Hu, H. (2022). Health consequences of exposure to lead and other toxic metals. The Lancet Planetary Health, 6(5), e427–e438. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00084-1
Li, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, H., & Wang, Q. (2022). Chemical speciation, bioavailability, and ecological risk of cadmium in agricultural soils: Influence of soil properties and anthropogenic inputs. Chemosphere, 291, 132928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132928
Li, X., Zhang, Y., & Chen, H. (2023). Application of geoaccumulation index and ecological risk assessment for evaluating heavy metal pollution in urban soils of China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45(6), 2479–2495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01477-4
Liu, X., Song, Q., Tang, Y., Li, W., Xu, J., Wu, J., Wang, F., & Brookes, P. C. (2023). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 249, 114407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114407
Mosley, L. M. (2024). Soil pH and its influence on trace element bioavailability: A global review. European Journal of Soil Science, 75(1), 21–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.70021
Ncube, N., Maseko, B., & Dube, T. (2021). Soil salinity and heavy metal interactions in landfill-contaminated soils of Southern Africa. Environmental Earth Sciences, 80, 694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09963-5
Obunwo, C. C., Ubah, S. C., Bull, O. S., & Amaibi, P. M. (2024). Solid-phase fractionation of heavy metal ions in soils from municipal waste dumpsite in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Journal of the Chemical Society of Nigeria, 49(1), 1 – 15
Ogunniyi, S. O., Afolabi, T. A., & Ojo, O. A. (2021). Assessment of enrichment factor and geoaccumulation index of heavy metals in soils around auto-mechanic workshops in Nigeria. Environmental Forensics, 22(5-6), 529–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2021.1922364
Okeke, A. C., Eze, P. N., & Ubah, S. C. (2024). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around open dumpsites in Southeastern Nigeria using Nemerow pollution index and risk assessment models. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31(15), 22567–22581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-29877-6
Olisa, O. G., Hashimi, A. M., Olatunji, O. T., Keyede, O. M., & Ajayi, O. A. (2024). Potentially toxic elements concentration and distribution in soils around artisan workshops in Ago-Iwoye, Southwestern Nigeria. Journal of Trace Elements and Minerals, 9, 100168.
Omoyajowo, K. O., Oladipo, O. G., & Oyeleke, S. I. (2023). Soil quality deterioration from dumpsites: Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment using PLI and geoaccumulation index. Scientific African, 20, e01621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2023.e01621
Patel, R., Singh, A., & Kumar, V. (2023). Speciation and bioavailability of nickel in contaminated soils: Influence of soil properties and redox conditions. Environmental Pollution, 316, 120489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120489
Rahimzadeh, M. R., Rahimzadeh, M. R., Kazemi, S., & Moghadamnia, A. A. (2017). Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Caspians Journal of Internal Medicine, 8(3), 135–145. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.8.3.135
Rahman, M. A., Hossain, M. S., & Akter, S. (2022). Evaluation of heavy metal accumulation and ecological risks in agricultural soils using pollution load index (PLI) and contamination indices. Chemosphere, 287(3), 132163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132163
Saha, R., Nandi, R., & Saha, B. (2023). Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium: A review. Chemosphere, 329, 138600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138600
Shabbir, Z., Qadir, I., & Ali, S. (2020). Copper uptake, essentiality, toxicity, detoxification and risk assessment in crops: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere, 258, 127159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127159
Shrivastava, R., Upreti, R. K., Seth, P. K., & Chaturvedi, U. C. (2022). Effects of chromium on human health and the environment. Environmental Pollution, 306, 119391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119391
Uchimiya, M., Bannon, D., Nakanishi, H., McBride, M. B., Williams, M. A., & Yoshihara, T. (2020). Chemical speciation, plant uptake, and toxicity of heavy metals in agricultural soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 68(46), 12856–12869.
Ukaogo, P. O., Eze, C. J., & Akpan, U. G. (2024). Heavy metal speciation and pollution indices of soils around auto-mechanic workshops in Enugu, Nigeria. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31(12), 16234–16247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-29564-7
Wang, Z., Luo, P., Zha, X., Xu, C., Kang, S., Zhou, M., Nover, D., & Wang, Y. (2022). Overview assessment of risk evaluation and treatment technologies for heavy metal pollution of water and soil. Journal of Cleaner Production, 379(Part 2), 134043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134043
Zhang, L., Xu, Y., & Gao, X. (2024). Soil organic matter and sesquioxides control copper retention and mobility in agricultural soils: Implications for ecological risk. Science of the Total Environment, 903, 166812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166812
Zulfiqar, U., Haider, F. U., Ahmad, M., Hussain, S., Maqsood, M. F., Ishfaq, M., Shahzad, B., Waqas, M. M., Ali, B., Tayyab, M. N., Ahmad, S. A., Khan, I., & Eldin, S. M. (2023). Chromium toxicity, speciation, and remediation strategies in soil-plant interface: A critical review. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, Article 1081624. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1081624
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Science Research and Reviews

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




